Monetary Diffusion in Bitcoin
Let me walk you through how OGs selling Bitcoin isn't a dump, but a crucial part of our Bitcoin economy that keeps the network healthy and growing.
OG’s selling is just another word for Bitcoin redistribution in the Bitcoin circular economy. All Bitcoins must eventually change hands for the holder to realize its value, as they must re-enter the market in exchange for goods and services. I call this process Monetary Diffusion.
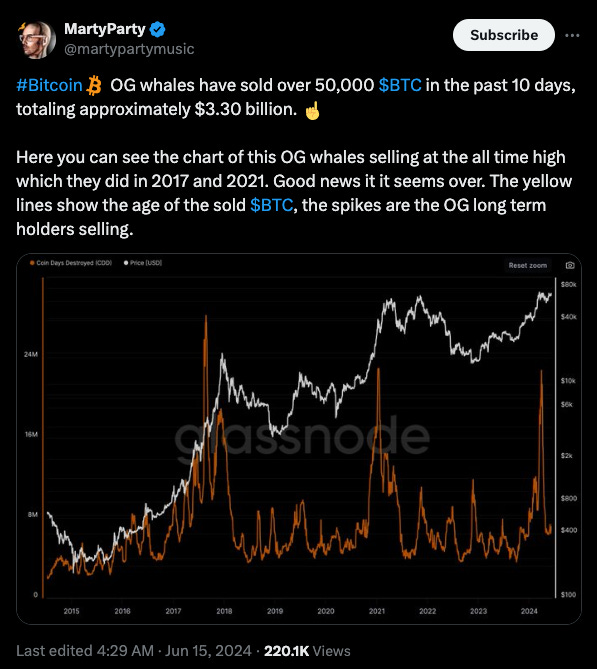
Recently, a tweet by Willy Woo highlighted that OG whales, who hold more Bitcoin than all ETFs combined, sold into the bull market. This pattern is as old as the genesis block. MartyParty echoed this, noting that OG whales sold over 50,000 BTC in the past 10 days, totaling approximately $3.30 billion. This activity is a prime example of Monetary Diffusion at work, showcasing how long-term holders participate in the economic cycle by redistributing their Bitcoin.
The comments on these tweets are mixed, with some suggesting that OGs are dumping Bitcoin on the market, likening it to a Ponzi scheme. This perspective misunderstands the fundamental dynamics at play. The act of OGs selling their Bitcoin is not about dumping; it’s about redistributing the currency within the Bitcoin network. This redistribution is essential for maintaining the liquidity and value of Bitcoin.
Understanding the Concept
People buy Bitcoin, hoping to increase their purchasing power. This frame is crucial. As the value of Bitcoin rises, traditional finance might describe this as making a profit. In Bitcoin, we call it choosing a longer-term preference, recognizing that it will increase purchasing power as Bitcoin diffuses and redistributes.
Monetary Diffusion is the process by which Bitcoin moves from one holder to another, particularly when early adopters or 'OGs' decide to sell their holdings. This movement is not just a simple transaction; it's an essential mechanism that supports the entire Bitcoin ecosystem.
When OGs sell their Bitcoin, they are effectively redistributing the money across the network participants. This redistribution helps to stabilize the market by spreading Bitcoin among a larger number of holders. As more people acquire Bitcoin, the network becomes more robust and resilient. Each transaction increases the network's overall liquidity, making it easier for others to buy and sell Bitcoin in the future.
This process is fundamental to the health of the Bitcoin economy. It ensures that Bitcoin does not remain concentrated in the hands of a few but is continually spread out to new users. As Bitcoin diffuses through these transactions, its value and utility are realized by a broader audience. This broader distribution contributes to the stabilization and growth of the market, encouraging more widespread adoption and acceptance of Bitcoin as a viable currency.
Additionally, this redistribution is a key component of Bitcoin's deflationary nature. Unlike fiat currencies, which can be printed at will, Bitcoin has a fixed supply. As Bitcoin becomes more scarce and its demand increases, the value of each Bitcoin is likely to rise. This incentivizes holders to choose a lower time preference, saving and holding their Bitcoin for longer periods, anticipating future gains in purchasing power.
Monetary Diffusion, therefore, is not just about selling Bitcoin for profit. It's about participating in an ongoing economic cycle that promotes the long-term health and sustainability of the Bitcoin network. By understanding and engaging in this process, Bitcoin holders contribute to a more decentralized, robust, and equitable financial system.
Time Preference and Bitcoin
Understanding time preference is crucial to grasping the concept of Monetary Diffusion. Time preference, a key idea explained by Saifedean Ammous in "The Bitcoin Standard," refers to the degree to which individuals value present consumption over future consumption. This concept helps us understand the economic behaviors and decisions that drive the Bitcoin market and its cyclical nature.
Time preference is central to Bitcoin literature because it influences how individuals approach savings, investment, and economic planning. A high time preference indicates a preference for immediate gratification, while a low time preference suggests a preference for delayed gratification and future benefits.
Economic Behavior and Savings:
Bitcoin is likened to gold as "hard money" that resists inflation and government interference. This stability encourages saving and long-term planning, thereby lowering individuals' time preference. People are more likely to hold onto their Bitcoin, anticipating its value will increase over time.
Delayed Gratification:
Saifedean Ammous argues that sound money like Bitcoin encourages long-term thinking and values the future over the present. Unlike fiat money, which loses value over time due to inflation, Bitcoin's deflationary nature promotes a lower time preference, encouraging holders to save and invest for the future.
Behavioral Economics:
Studies show that Bitcoin holders with long-term horizons tend to prioritize future rewards over immediate ones, indicating a lower time preference. This behavior supports the idea that Bitcoin is a tool for long-term wealth preservation rather than quick profit.
Historical and Theoretical Context:
The time preference theory of interest explains how preferences for present consumption over future consumption influence interest rates and economic decisions. Bitcoin, as sound money, lowers societal time preference, fostering a culture of savings and investment that can lead to broader economic stability and growth.
Practical Applications:
The practice of "hodling" (holding onto Bitcoin despite market volatility) is seen as an embodiment of low time preference. Bitcoin holders trust in the currency's long-term value, which aligns with the principles of Monetary Diffusion by ensuring that Bitcoin remains in circulation and gradually redistributes through the economy.
Philosophical and Societal Implications:
Investing in Bitcoin today is akin to planting trees for future generations. This metaphor highlights the long-term benefits of a low time preference, where current investments yield significant future rewards, contributing to the overall health and sustainability of the Bitcoin economy.
By understanding time preference, we gain insights into the behaviors that underpin Monetary Diffusion. Low time preference drives individuals to hold and eventually redistribute their Bitcoin, supporting a stable and growing Bitcoin economy. This cyclical process of saving and spending ensures that Bitcoin remains a robust and dynamic financial system, reinforcing its value and utility over time.
The Bitcoin Circular Economy
The Bitcoin Circular Economy (BCE) revolves around conducting all economic activities within the Bitcoin ecosystem itself, using Bitcoin as the primary medium of exchange. This model aims to create a self-sustaining economic system where Bitcoin is used for all transactions, minimizing reliance on traditional financial systems and fiat currencies.
Unlike fiat economies, which are dependent on centralized control and intermediaries, the Bitcoin Circular Economy operates on the principles of decentralization and peer-to-peer interactions. This ensures that transactions are secure, transparent, and immutable, all finalized by on-chain settlement.
Key Aspects of Bitcoin Circular Economy
On-Chain Transactions:
Transactions occur on the Bitcoin blockchain, also known as the timechain, ensuring sequential, transparent, and immutable records. This on-chain settlement is the final step that guarantees the security and authenticity of each transaction.
Decentralization and Peer-to-Peer Transactions:
BCEs facilitate direct transactions between parties without intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. The Lightning Network, a second-layer solution, allows for faster and cheaper transactions, while still ultimately being settled on-chain.
Economic Autonomy and Independence:
Using Bitcoin as the primary currency provides increased economic independence, especially beneficial for the unbanked and underbanked populations. This autonomy allows individuals and communities to participate in the global economy without the barriers imposed by traditional financial systems.
Sustainability and Resource Efficiency:
BCEs align with the principles of a circular economy, emphasizing reusing, recycling, and repurposing resources to minimize waste. Bitcoin's transparent ledger and immutable records support efficient resource management and accountability.
Wealth Redistribution:
Bitcoin rewards early adopters who eventually spend their Bitcoin on meaningful goods and services, ensuring value circulation and fair wealth redistribution. This process encourages continuous economic activity and growth within the Bitcoin network.
Examples of Bitcoin Circular Economies
Bitcoin Beach, El Salvador:
Locals use Bitcoin for everyday transactions, promoting financial inclusion and economic growth. This community has built a sustainable economy where Bitcoin is the primary medium of exchange.
Plan ₿, Lugano, Switzerland:
An initiative to create a Bitcoin-based economy, promoting Bitcoin for various transactions. This model showcases how a local economy can thrive using Bitcoin, independent of the traditional financial system.
Bitcoin Ekasi, South Africa:
A non-profit organization establishing a Bitcoin-based economy in a disadvantaged area, empowering the local community through Bitcoin transactions. This initiative highlights the potential for Bitcoin to drive economic development and inclusion.
Broader Implications and Interoperability
The Bitcoin network is fundamentally different from the fiat economy. It functions as one large circular economy where people can create smaller, sustainable economies within it. These local economies can trade and conduct commerce with each other in an interoperable manner, without needing to trust one another. This trustless system is a hallmark of the broader Bitcoin network, facilitating global commerce and economic interactions seamlessly.
As more people opt out of the fiat system and build new systems and economies, we see the proliferation of these Bitcoin circular economies worldwide. These models represent a shift towards decentralized, transparent, and self-sustaining economic systems.
The Role of OGs in the Bitcoin Circular Economy
The concept of Monetary Diffusion comes full circle when considering the role of OGs in the Bitcoin Circular Economy. OGs selling their Bitcoin into the economy is beneficial and should be encouraged. They are the capital allocators within the Bitcoin Circular Economy, and their spending drives future economic activity. Each transaction they make helps to redistribute Bitcoin and stimulate growth within the network.
Every halving epoch brings a new generation of Bitcoiners, continuing the cycle of wealth redistribution and economic development. OGs, having achieved their financial goals, pass on their Bitcoin to newer market participants. This ongoing process is akin to a game of musical chairs with money, where each generation contributes to the stability and expansion of the Bitcoin economy.
By understanding and participating in the Bitcoin Circular Economy, we support a robust and dynamic financial system that aligns with the principles of decentralization, transparency, and individual empowerment. This is the future of economic activity, driven by the collective efforts of Bitcoin holders worldwide.
Conclusion
The concept of Monetary Diffusion is integral to understanding how Bitcoin operates within its unique economic framework. As highlighted, the act of OGs selling their Bitcoin is not merely about liquidating assets for profit. Instead, it represents a critical redistribution mechanism that supports the health and stability of the Bitcoin network. This process ensures that Bitcoin circulates among a broader and more diverse group of users, reinforcing the decentralized nature of the system.
By embracing a lower time preference, Bitcoin holders are encouraged to save and hold their Bitcoin, anticipating future increases in purchasing power. This behavior fosters a culture of long-term thinking and investment, which is essential for the sustained growth of the Bitcoin economy.
The Bitcoin Circular Economy exemplifies how a decentralized and transparent financial system can function. With on-chain transactions ensuring security and transparency, and second-layer solutions like the Lightning Network facilitating efficient transactions, Bitcoin provides a viable alternative to traditional fiat systems. Local Bitcoin economies, such as those in El Salvador, Switzerland, and South Africa, showcase the real-world potential of this model to promote financial inclusion and economic development.
OGs play a pivotal role in this ecosystem. Their spending not only redistributes wealth but also drives future economic activity within the Bitcoin network. Every halving epoch introduces a new generation of Bitcoiners, continuing the cycle of wealth redistribution and economic growth. This process ensures that Bitcoin remains dynamic and resilient, capable of adapting and thriving as more people join the network and opt out of the fiat system.
Ultimately, each cycle brings us closer to Hyperbitcoinization with every halving epoch, triggering Monetary Diffusion events. These events occur as more individuals learn about Bitcoin and choose to save in it.. This ongoing process strengthens the broader Bitcoin network, paving the way for a more equitable and transparent financial future. By participating in the Bitcoin Circular Economy, we contribute to a robust financial system that embodies the principles of decentralization, transparency, and individual empowerment. This is the path forward, driven by the collective efforts of Bitcoin holders worldwide, ensuring the continued evolution and success of the Bitcoin ecosystem.